- There are two ways woman can prevent cervical cancer: Pap tests and the HPV vaccine-Gardasil 9.
- Pap tests are exams used to screen for cervical cancer. Women between the ages of 25 to 69 should be screened every 3 years.
Speculum icon in flat style isolated on white background. Pregnancy symbol vector illustration.

- If abnormal cells are found and treated early, it can stop the cells from becoming cancerous. Also, cancerous cells can be identified at an early stage and treated. Because of this Pap tests are saving lives.
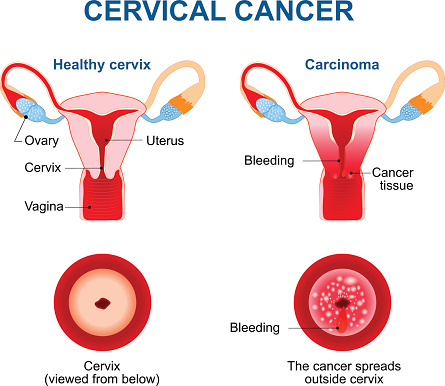
- Cervical cancer symptoms include: abnormal vaginal bleeding, abnormal or persistent vaginal discharge, pelvic pain or pain during intercourse, but most of the time cervical cancer has no symptoms.
- HPV human papillomavirus infection causes almost all cervical cancer. Usually HPV is removed from the body by the immune system within 2 years, but sometimes cells are not removed. This process can take up to 10 years and can progress to pre-cancerous cells or cervical cancer.
- HPV is very common and easily spreads through sexual contact.
Pap Tests
- During a Pap test a speculum (image below) is inserted into the vagina in order for the health care professional to see the cervix. They will collect cells from your cervix using a small brush or spatula. This procedure can be uncomfortable but should not be painful.
- Pap tests can be done by a doctor, nurse practitioner, registered nurse, midwife or naturopathic doctor.
- The test should only take about 5 minutes.
- Pap tests are free.

Speculum used during PAP smear sample collection
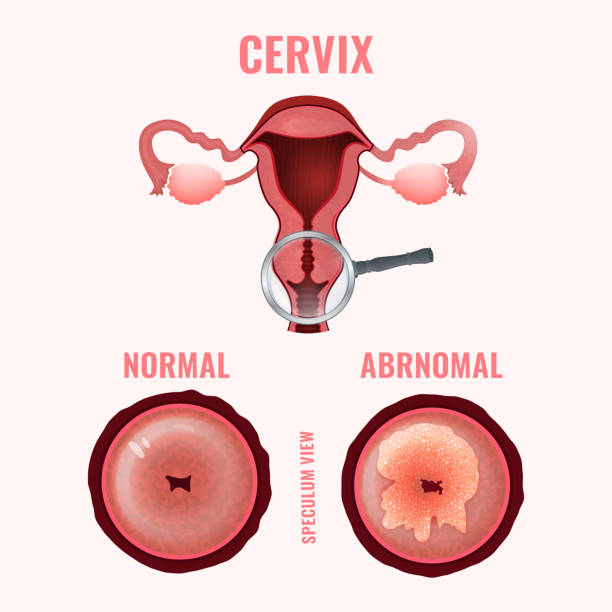
Abnormal Results
- An abnormal Pap test means the cells in your cervix do not look normal.
- These results are common and do not mean cancer.
- Follow up will be determined on what type of cell changes are present: mild atypical cell changes or moderate to severe atypical cell changes.
- Mild atypical cell changes usually return to normal. Your doctor will repeat screening in 6 months.
- Moderated to severe atypical cell changes are less likely to return to normal. Your doctor will refer you for a colposcopy.
Colposcopy
- It is a procedure to examine your cervix and vagina.
- A colposcope (microscope) is used to look for abnormalities.
- The test begins much like a Pap test, a speculum is gently inserted into the vagina to get a better look at your cervix.
- Vinegar or iodine may be applied to make abnormalities more visible on your cervix.
- During the colposcopy the health care professional may take tissue from abnormal looking areas on the cervix. This is called a biopsy.
- Results are available between 2 and 4 weeks.
- The procedure should be done in 5 to 10 minutes.
- Colposcopy results show either low-grade or high-grade cell changes.
- Low-grade (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 1, or CIN1). These are minor cell changes that often correct themselves and treatment is not typically needed.
- High-grade (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or 3, or CIN 2, CIN 3). These cell changes can become cancerous. Your health care provider will suggest a LEEP procedure.
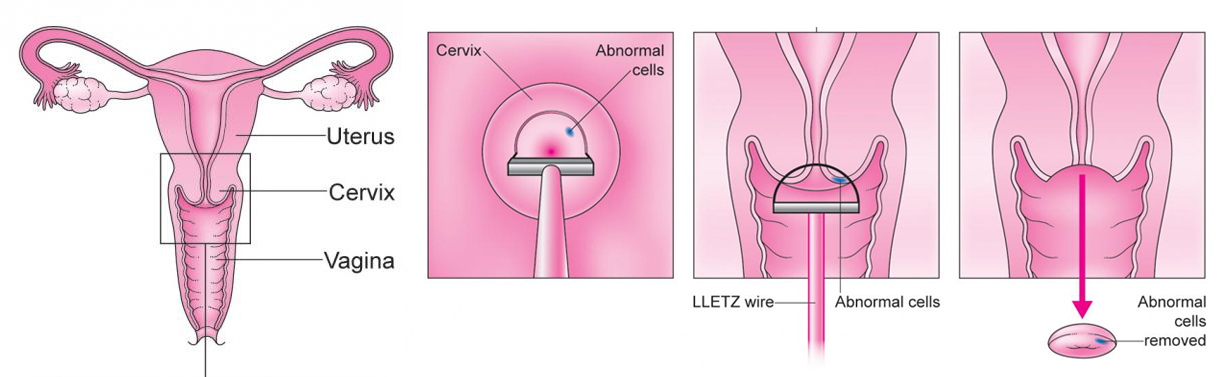
LEEP-Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure
- Your health care professional may recommend a LEEP procedure if you receive an abnormal colposcopy.
- A LEEP procedure involves removing abnormal tissue from your cervix with a thin wire loop.
- The health care professional will use a microscope (colposcope) to look at your cervix.
- Vinegar or iodine will be used to make any abnormalities on your cervix more visible.
- Freezing is used to numb the cervix and a thin wire loop is used to removal abnormal tissue.
- A brown paste may be placed in the cervix to reduce any bleeding.
- Procedure usually lasts about 5 minutes.
- A colposcopy is usually done 6 months after your LEEP procedure. A tissue sample will be taken (biopsy) and will be checked for HPV.
- Normal test results: very low risk of developing further abnormalities.
- Abnormal test results: a second LEEP procedure is required. Have a higher risk of developing further abnormalities.
- LEEP procedure can remove cells in your cervix containing HPV.
Cervical Cancer Prevention
- The best way to protect yourself from cervical cancer and HPV infections is to get the Gardasil 9 vaccine (3 doses).
- Gardasil 9 protects against HPV related cancers such as cervical cancer.
- Another way to protect yourself is to get a Pap test every 3 years if you are between the ages of 25-69.
- If found early cervical cancer is 85% curable.
Gardasil 9
- The Gardasil 9 vaccine protects against HPV. The vaccine consists of 7 HPV types that cause cervical cancer and 2 HPV types that cause genital warts.
- HPV is responsible for almost 100% of cervical cancers.
- Gardasil 9 can protect woman from cervical, anal, vaginal, vulvar and oropharyngeal cancer as well as genital warts.
- Gardasil 9 can protect men from penile, anal, oropharyngeal cancer as well as genital warts.
- Gardasil 9 is a 3 dose series at 0, 2, and 6 months.
- Gardasil 9 works by helping your immune system make antibodies against the 9 HPV types in the vaccine. If you’re exposed to one of these types, the antibodies help defend against developing an infection and related diseases such as cancer.
- Gardasil 9 can be given to men and women ages 9 to 45.
References:
Photo References:
https://majeedhealth.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2021/04/4295493-1024×683.jpg
https://womenobgyn.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/LEEP_.jpg
https://cdn2.poz.com/62204_CHWi-19-030.jpg_c05d10d0-7e80-4124-b95e-7d2a29f9df32.jpeg
https://nci-media.cancer.gov/pdq/media/images/609927.jpg
